Rotational Equations Of Motion
This derivation is based on the properties of a velocity time graph for uniformly accelerated motion where the slope of the graph represents the acceleration.

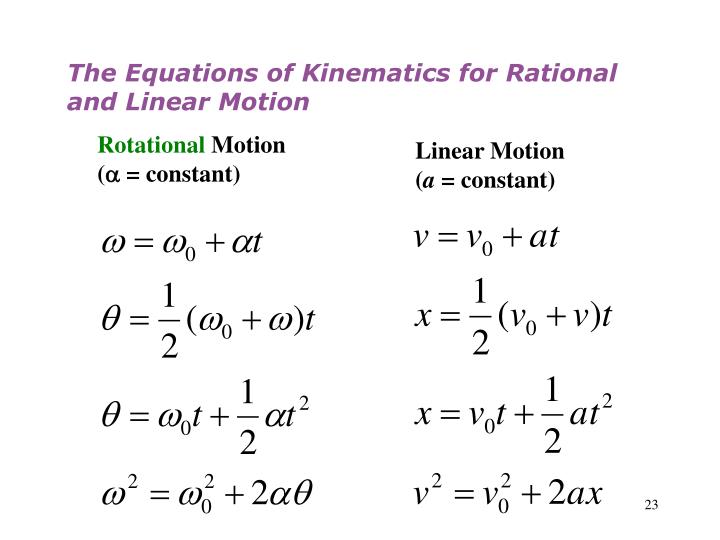
Rotational equations of motion. Rotation is described in terms of angular displacement time angular velocity and angular acceleration. Angular velocity is the rate of. Rotation around a fixed axis or about a fixed axis of revolution or motion with respect to a fixed axis of rotation is a special case of rotational motion. In physics equations of motion are equations that describe the behavior of a physical system in terms of its motion as a function of time.
More specifically the. Torques and rotational motion just as net forces cause changes in translational motion net torques cause changes in rotational motion. The logic behind setting these. Then we must also place it in a state of rotational equilibrium where the sum of all of the torques equals zero.
For horizontal beams in the plane of the page the.